Sign up for our newsletter to get the latest news, announcements and special offers
Help Stop the Spread
Since the beginning of the coronavirus outbreak, we have been urged to pay attention to our hand hygiene — and for good reason. Handwashing is one of the most important things you can do to help slow or reduce the spread of the virus, and help keep you and your family safe.


How hands spread coronavirus
COVID-19 is primarily spread through social interaction. If a healthy person comes face to face with an infected person, they may contract the virus through contaminated droplets spread by coughing or sneezing.
Your hands can be a major source of infection: the tiny droplets that hang in the air after a cough or sneeze may settle on surfaces such as counter tops, tables or even door handles, contaminating them.
If you touch your face after touching these surfaces you may also contract the virus.
When to wash
Hand hygiene is key. It is important to wash your hands³:
- Whenever you touch something that may be contaminated
- If you touch someone who is sick with COVID-19
- After you use the bathroom
- Before eating, and before, during and after preparing food
- After blowing your nose, sneezing or coughing
- Before and after tending to a sick person, or a baby
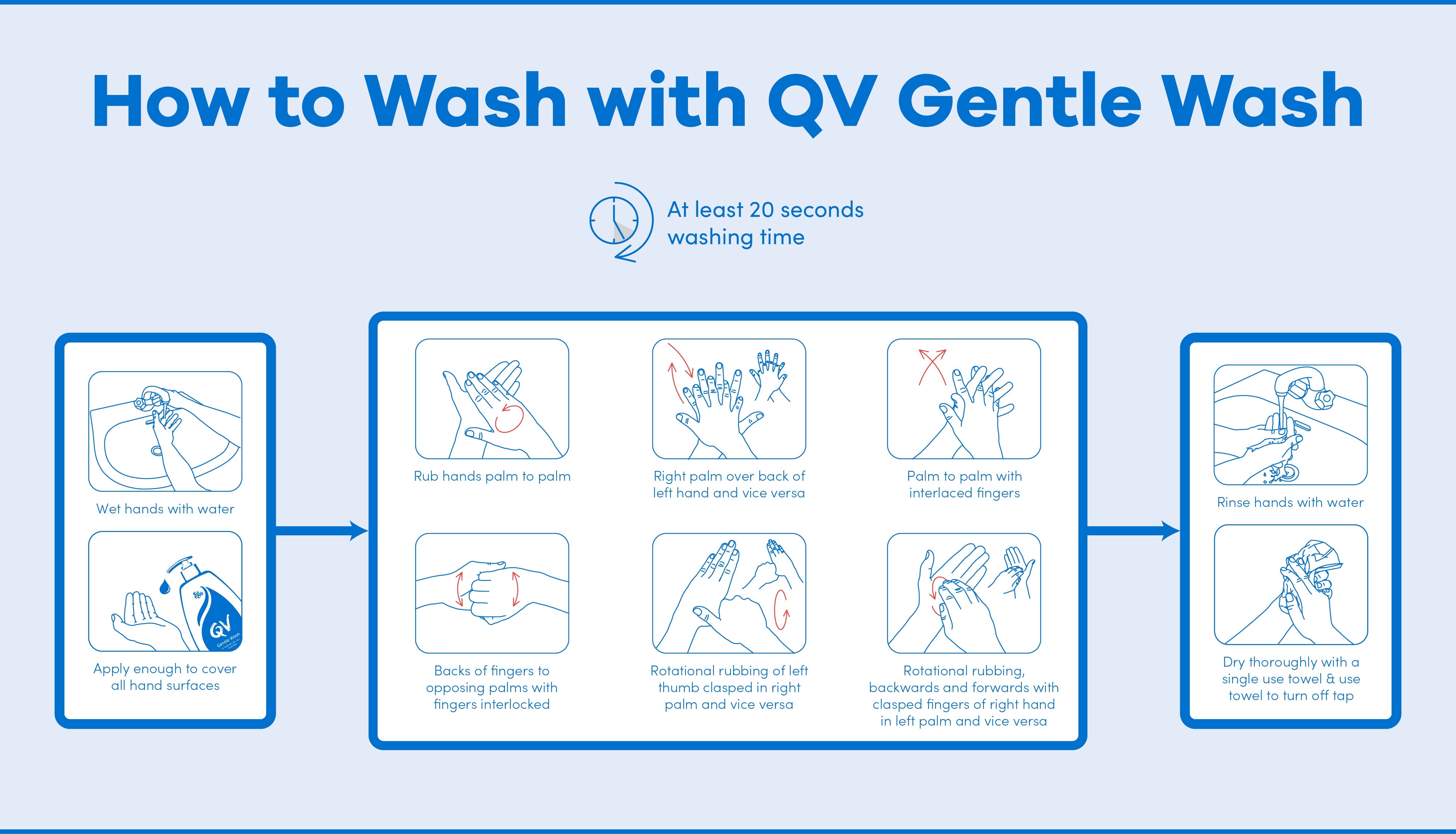



Why a non-soap based cleanser? What about soap?
Soap and non-soap based cleansers do exactly the same thing; they clean the skin. A key difference though is the type of ingredient used to do this. Soap is formed though a chemical process known as saponification, which is a reaction between strong bases. This reaction leaves the soap highly alkaline, which means that it usually has a pH of around 9 or 104. The skin itself has a natural pH of around 5, so an alkaline product like soap can alter the skins composition5 and potentially lead to irritation. Non-soap based cleansers such as QV Gentle Wash contain synthetic detergents in place of soap. As the process doesn’t need to be highly alkaline, like soap, the pH of these products can be closer to that of the skin. What this means is that non-soap based cleansers will work just as well as soap without aggravating your skin.
Why Handwashing is best, then hand sanitiser.
Washing your hands properly with water and soap or a gentle non-soap based cleanser such as QV Gentle Wash is one of the best ways to help prevent COVID-19. Soap and cleansers work by lifting dirt and contaminants like bacteria and viruses from the skin. The mechanical action of hand washing also plays a part; the act of rubbing your hands together can help to lift contaminants from the skin. In fact, the mechanical action of washing your hands is a major reason why cleansing with water and soap or a non-soap based cleanser is the preferred method. While hand sanitisers can be effective against germs such as bacteria, they cannot remove dirt and grime from the hands. The best advice is to wash your hands thoroughly with water and soap or a non-soap based cleanser for at least 20 seconds whenever you can. When this isn’t an option, keep a hand sanitizer such as Aqium close at hand.
References:
- WebMD. The Power of Hand-Washing to Prevent Coronavirus. 2020 [internet]. 06/03/2020. Retrieved 18/03/2020. Available from: https://www.webmd.com/lung/news/20200306/power-of-hand-washing-to-prevent-coronavirus
- NSW Government. Health. Infectious Diseases. COVID-19- Frequently Asked Questions. 2020 [internet]. ]. Updated 18/03/2020, retrieved 18/03/2020. Available from: https://www.health.nsw.gov.au/Infectious/alerts/Pages/coronavirus-faqs.aspx#1-3
- CDC. Handwashing. When and how to wash your hands. 2019 [internet]. Last reviewed 03/10/2019, retrieved 18/03/2020. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/handwashing/when-how-handwashing.html
- Tarun J, Susan J, Suria J, Susan VJ, Criton S. Evaluation of pH of bathing soaps and shampoos for skin and hair care. Indian J Dermatol 2014;59(5):442-444
- Lambers H, Piessens S, Bloem A, Pronk H, Finkel P. Natural skin surface pH is on average below 5, which is beneficial for its resident flora. Int J Cosmet Sci 2006;28(5):359-70